|
|
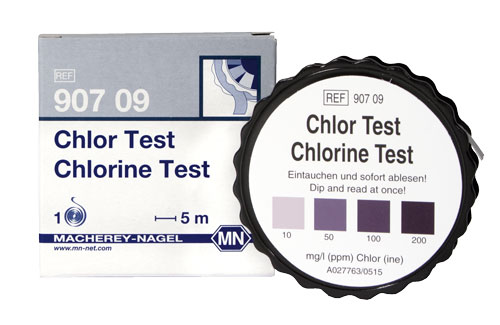
Chlorine Test paper |
Semi-quantitative test paper |
0 · 10 · 50 · 100 · 200 mg/L Cl2 |
90709 |
|
Semi-quantitative test paper for the determination of chlorine. The test is particularly suitable for high range applications in disinfectant solutions which are for example used in food and beverage industry and animal farms.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Color reaction: white → blue-violet
Scope of delivery: 1 reel of 5 m length and 10 mm width
|
|
|
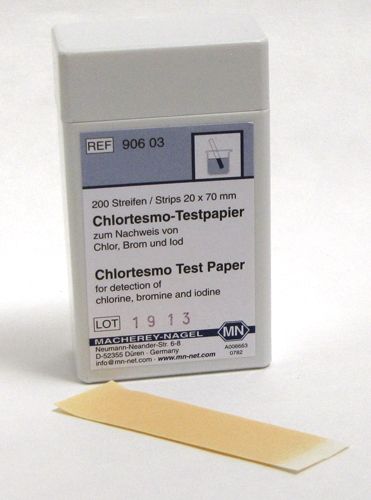
Chlortesmo |
Qualitative test paper |
1 mg/L Cl2 |
90603 |
|
This test paper allows the quick and easy detection of free halogens (chlorine, bromine, iodine). Free nitrous acid HNO2 (not nitrite ions) interferes, but can be destroyed by addition of amidosulphuric acid.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Color Reaction: pale yellow → blue
Scope of delivery: 200 test strips in a plastic box
|
|
|
Chlorine Test strip |
Semi-quantitative test paper |
0 · 2 · 10 · 50 · 100 · 200 mg/L total chlorine |
90633 |
|
Semi-quantitative test strips for the determination of total chlorine.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Scope of delivery: Tube of 200 strips
|
|
|
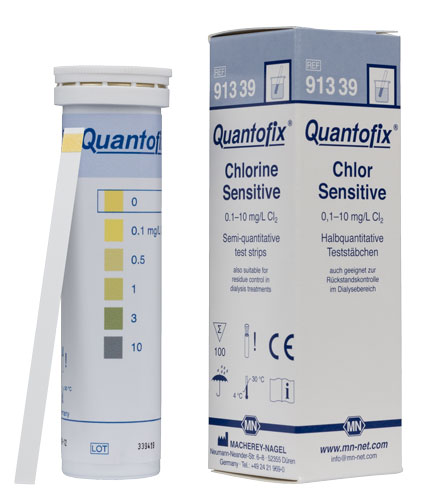
QUANTOFIX® Chlorine Sensitive |
Semi-qualitative test strips |
0 · 0.1 · 0.5 · 1 · 3 · 10 mg/L Cl2 |
91339 |
|
These test strips allow the quick and easy detection of low range total Chlorine (total chloramines). The easy dip-and-read procedure provides reliable results within 20 sec. QUANTOFIX® Chlorine Sensitive test strips are the perfect choice when it is necessary to determine low range chlorine.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Color Reaction: yellow → violet
Scope of delivery: 100 test strips in a tube, instruction leaflet
|
|
|
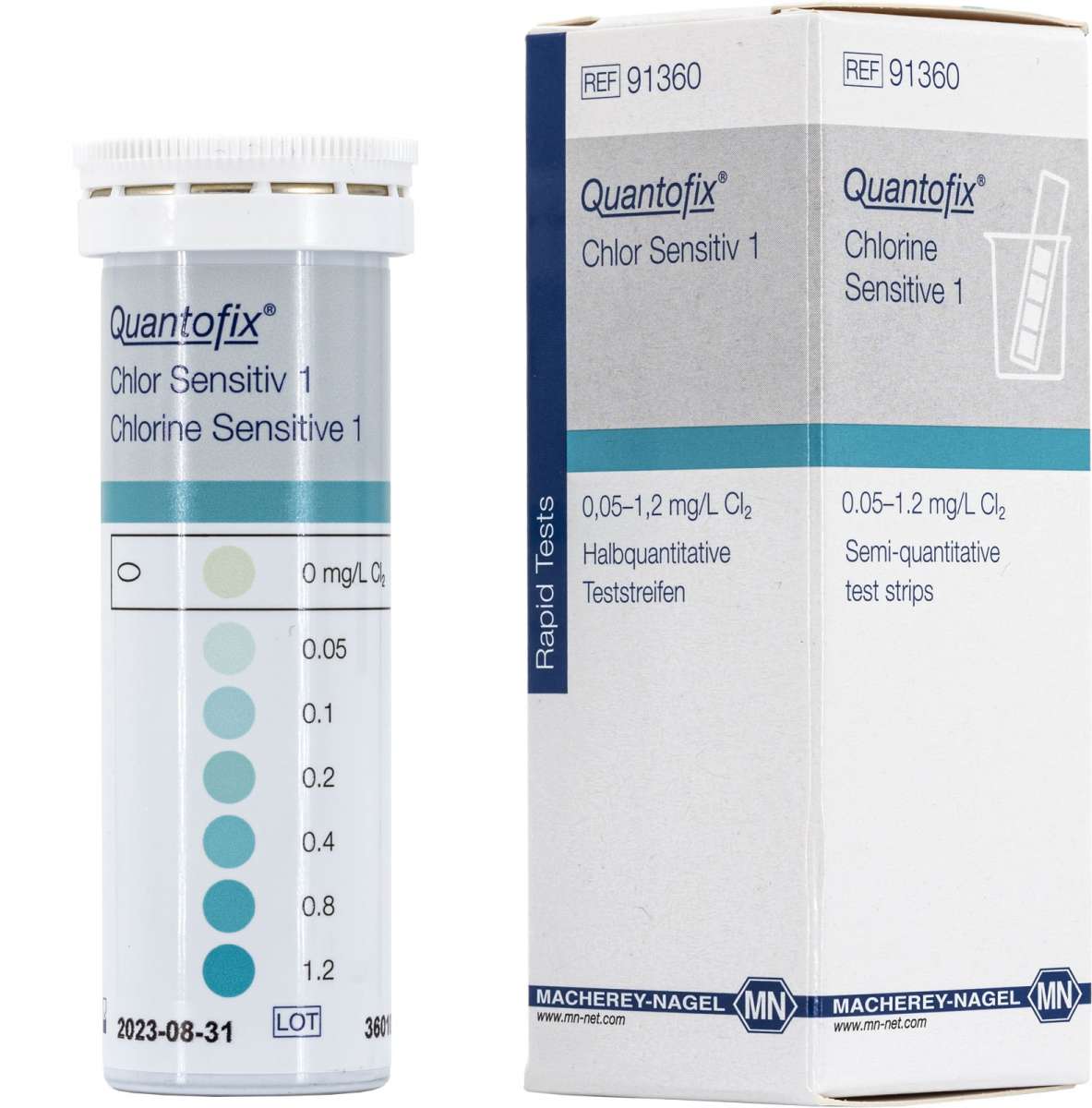
QUANTOFIX® Chlorine Sensitive 1 |
Semi-quantitative test strips |
0 · 0.05 · 0.1 · 0.2 · 0.4 · 0.8 · 1.2 mg/L Cl2 |
91360 |
|
This test allows the quick and easy determination of Chlorine in solutions. It comes with all necessary reagents so that the measurement can immediately be started. Within 1 minute one gets a reliable result.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Color Reaction: white → blue-green
Scope of delivery: 50 test strips in a tube, instruction leaflet
|
|
|
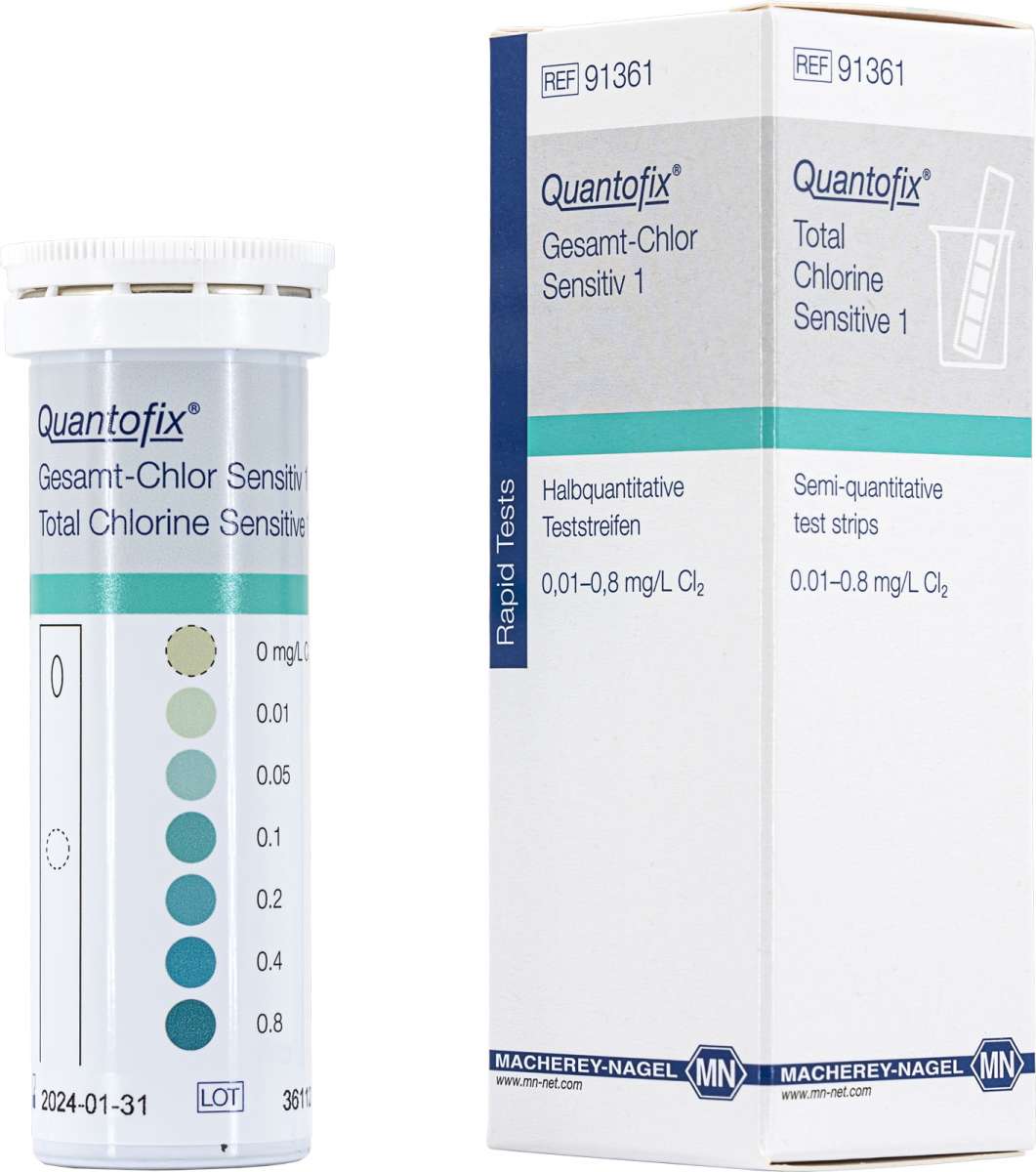
QUANTOFIX® Total Chlorine Sensitive 1 |
Semi-qualitative test strips |
0 · 0.01 · 0.05 · 0.1 · 0.2 · 0.4 · 0.8 mg/L Cl2 |
91361 |
|
Test sticks for the semi-quantitative determination of total chlorine concentrations as low as 0.01 mg/L (ppm). A hole in the plastic carrier allows the water to migrate through the test pad, providing a high level of sensitivity.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Color Reaction: white → blue-green
Scope of delivery: 50 test strips in a tube, instruction leaflet
|
|
|
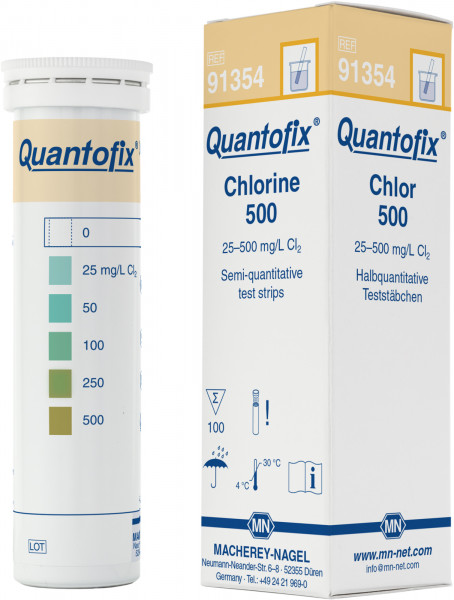
QUANTOFIX® Chlorine 500 |
Semi-quantitative test strips |
0 · 25 · 50 · 100 · 250 · 500 mg/L Cl2 |
91354 |
|
Semi-quantitative test strips for the determination of chlorine. Ideal for rapid and easy analysis of chlorine directly on-site. No maintenance or calibration is required.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Color Reaction: white → blue-green to orange-brown
Scope of delivery: 100 test strips in a tube, instruction leaflet
|
|
|
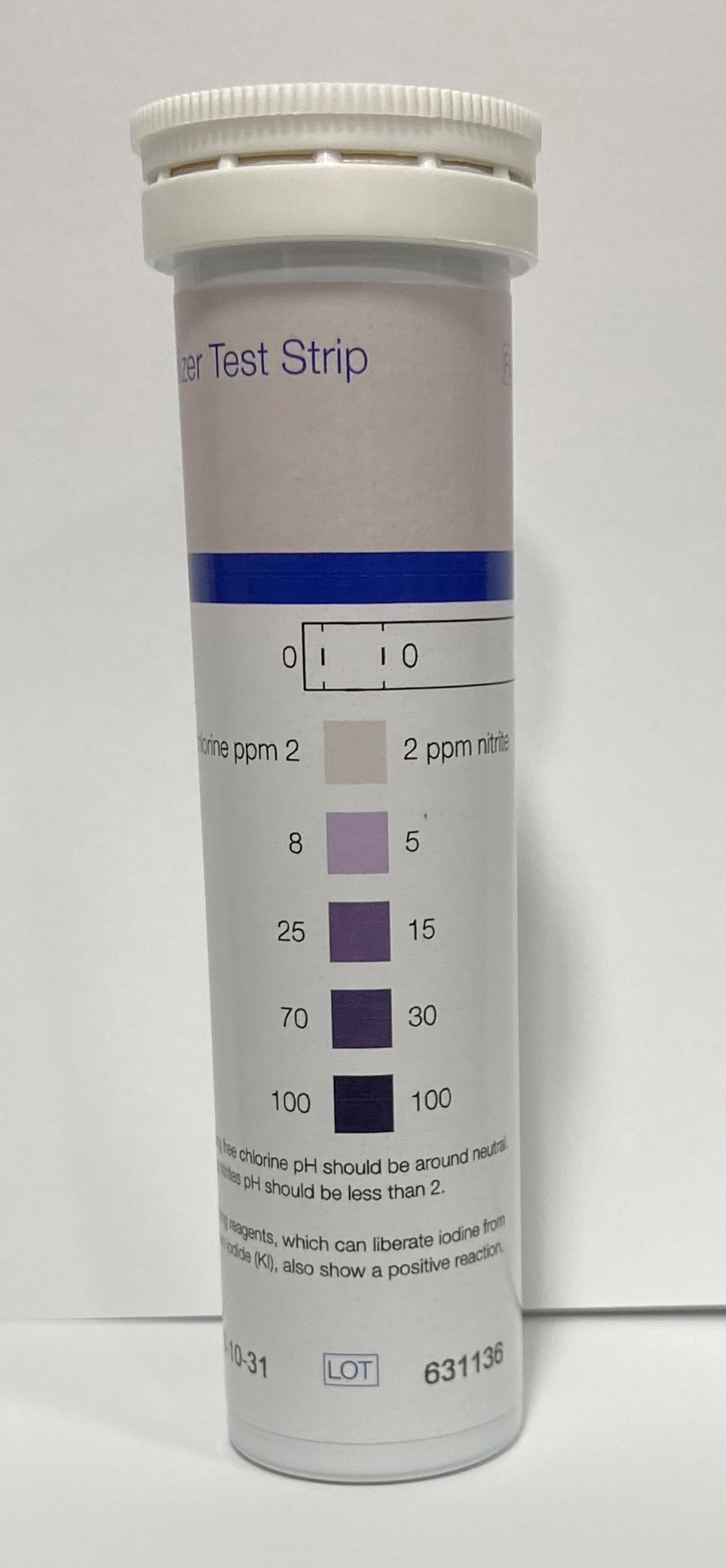
Oxidizer Test Strips/Potassium Iodide Starch Paper |
Semi-qualitative test strips |
0 · 2 · 8 · 25 · 70 · 100 mg/L free Cl2 |
90631 |
|
Semi-quantitative test strips for the detection of chlorine and nitrite. Color chart with 5 steps from 2 to 100 ppm.
Scope of delivery: Tube of 100 strips
|
|
|
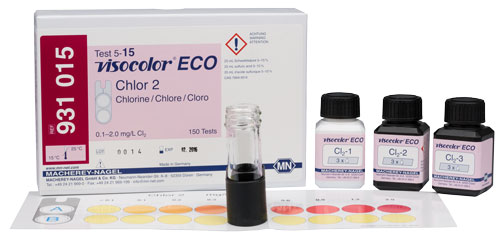
VISOCOLOR® ECO Chlorine 2, Free and Total |
Colorimetric test kit |
<0.1 · 0.1 · 0.2 · 0.3 · 0.4 · 0.6 · 0.9 · 1.2 · 2.0 mg/L Cl2 |
931015 |
|
Colorimetric test kit for the determination of Chlorine in water samples. VISOCOLOR ECO Chlorine 2, free and total combines easy performance with high measurement safety, by color and turbidity compensation. For visual determination by comparison with a color chart or photometric measurement with our compact photometers.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Sea water analysis: No
Scope of delivery: Reagents for 150 tests, color chart and accessories in a box
|
|
|
VISOCOLOR® ECO Chlorine 2 |
Photometric test paper |
<0.1 · 0.1 · 0.2 · 0.3 · 0.4 · 0.6 · 0.9 · 1.2 · 2.0 mg/L Cl2 |
931016 |
|
Colorimetric test kit for the determination of Chlorine in water samples. VISOCOLOR ECO free Chlorine 2 combines easy performance with high measurement safety, by color and turbidity compensation. For visual determination by comparison with a color chart or photometric measurement with our compact photometers.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Sea water analysis: No
Scope of delivery: Reagents for 150 tests, color chart and accessories in a box
|
|
|
VISOCOLOR® Powder Pillows Free Chlorine For use on photometers |
Photometric test paper |
0.03 - 6.00 mg/L Cl2 |
936220 |
|
Reagent powder pillows for photometric determination of free chlorine. Powder pillows combine easy dosing with Photometric precision. Ideal for pool or drinking water analysis.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Sea water analysis: Yes
Scope of delivery: 100 Powder Pillows in a bag
|
|
|
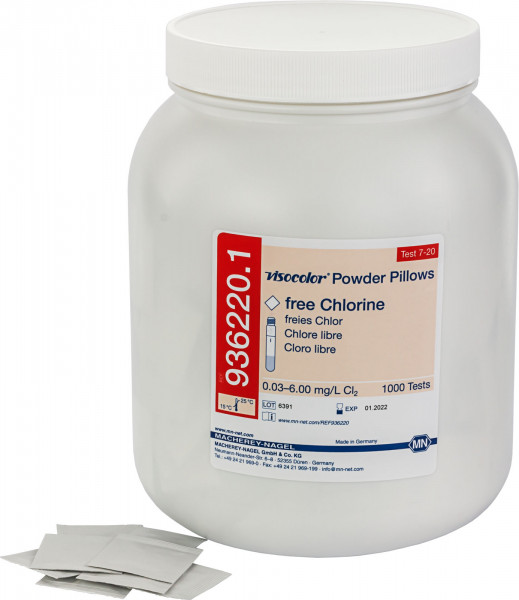
VISOCOLOR® Powder Pillows Free Chlorine for use on photometers |
Photometric test paper |
0.03 - 6.00 mg/L Cl2 |
936220.1 |
|
Reagent powder pillows for photometric determination of free chlorine. Powder pillows combine easy dosing with photometric precision. Ideal for pool or drinking water analysis.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Sea water analysis: Yes
Scope of delivery: 1000 Powder Pillows in a bag
|
|
|
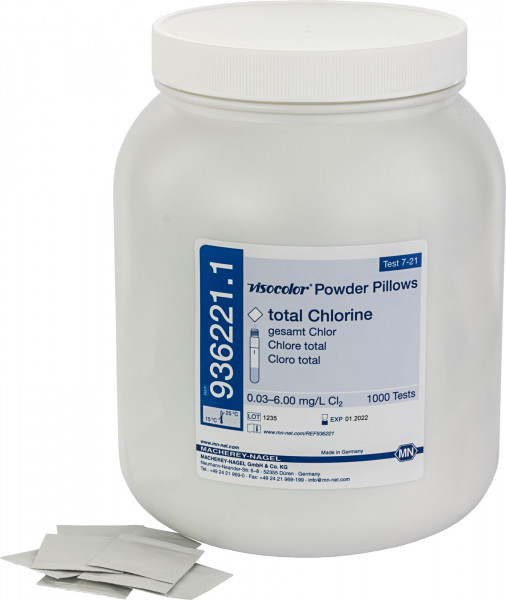
VISOCOLOR® Powder Pillows Total Chlorine for use on photometers |
Photometric test paper |
0.03 - 6.00 mg/L Cl2 |
936221 |
|
Reagent powder pillows for photometric determination of total chlorine. Powder pillows combine easy dosing with photometric precision. Ideal for pool or drinking water analysis. Total Ozone can also be determined from 0.03 - 4.00 mg/L.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Sea water analysis: Yes
Scope of delivery: 100 Powder Pillows in a bag
|
|
|
VISOCOLOR® Powder Pillows Total Chlorine for use on photometers |
Photometric test paper |
0.03 - 6.00 mg/L Cl2 |
936221.1 |
|
Reagent powder pillows for photometric determination of total chlorine. Powder pillows combine easy dosing with photometric precision. Ideal for pool or drinking water analysis. Total Ozone can also be determined from 0.03 - 4.00 mg/L.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Sea water analysis: Yes
Scope of delivery: 1000 Powder Pillows in a bag
|
|
|
NANOCOLOR® Chlorine/Ozone 2 |
Photometric tube test |
0.05 - 2.50 mg/L Cl2 |
985017 |
|
Tube test for the determination of Chlorine and Ozone. Precise rapid tests for all kind of water and waste water samples. Time-saving and reliable analysis together with our NANOCOLOR photometers.
Instruction Sheet (pdf)
Sea water analysis: Yes
Scope of delivery: Rugged box with 20 test tubes. Sufficient for 20 tests
|